One of the most common conditions sustained in a car accident or workplace incidents is knee injuries. Deficits to the knee can hugely impact your life, such as the ability to walk, work and even perform simple daily activities. For more severe injuries, you can be left with permanent disabilities and limitations.
Fortunately, most knee injuries are manageable with the appropriate medical treatment. However, your recovery can take up valuable time and finances. During these hardships, it’s essential to find compassionate and experienced compensable consultants.
Under the guidance of a relevant health professional, most knee injuries can be managed effectively. For additional support, our article below will go through some essential information, such as a brief description of your injury and the treatments available.
Mike Lombardi Injury Attorneys understand that these deficits can be a burden on your current lifestyles, such as your personal relations and financial situation. We aim to help you through these tough times and assist you with the compensation that you deserve. Please visit https://www.lombardilawoffice.com/ or call/text, Mike Lombardi, on 401-600-0000 for further assistance.
Common Knee Injuries
Whether it’s a high-impact car accident or awkward fall at work, a sudden knee injury can often take months and sometimes years to recover. Depending on factors, such as how the injury occurred and the location of the injury, your prognosis will vary. Some may experience two or more concurrent injuries, while others only minor deficits. Below are a few common compensable knee injuries which you may have.
Knee sprains (e.g. ACL, MCL tears etc.)
A sprain means that the ligament has been compromised. Ligaments are fibrous bands of tissue which attach on either side of a joint. The role of the ligament is to help stabilize and provide feedback to the joint. For example, the ACL attaches within the knee joint and prevents excessive movement between the two bones it connects to (femur and tibia).
Sprains are classified into three grades which determine the extent of the injury. The injury’s grading will help dictate how you will be medically managed.
For the knee, there are four main ligaments which work together to stabilize the knee. The ACL, PCL, MCL and LCL are in various locations around the knee to resist specific directional forces. If one or more of these ligaments are torn, the knee can feel unstable and “giving way.”
Depending on the severity of your knee sprain, you may experience the following symptoms:
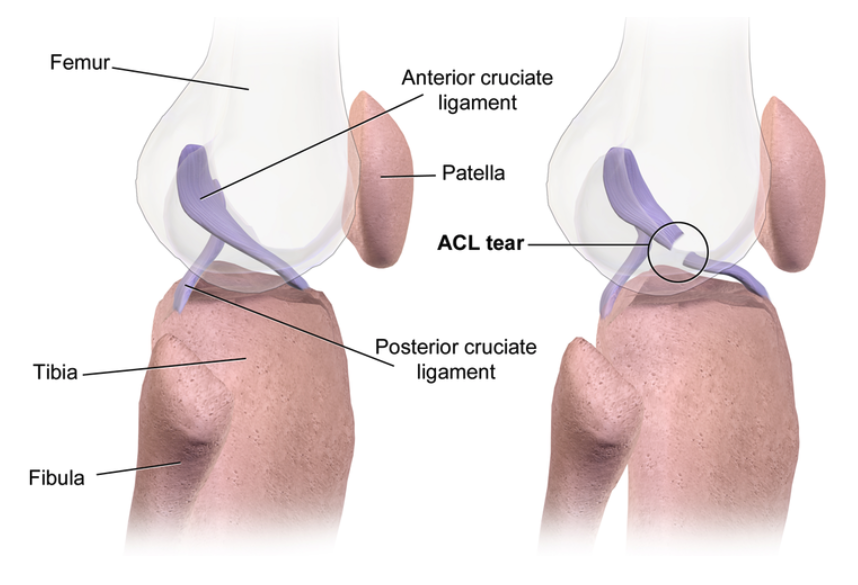
Image 1. A graphic representation of an ACL rupture. Source.
Meniscus Tears
Within the knee joint are the medial and lateral meniscus. They are composed of pieces of cartilage which helps guide movement and absorb your body’s weight. Clinically, most injuries seen are due to traumatic injuries, particularly with actions such as sudden bending and twisting of the knee. These types of injuries can occur during common activities such as lifting heavy items or even landing awkwardly after tripping. However, in older populations meniscus injuries can be from degenerative changes due to accumulated stress through the knee. The location (image 2) and severity of the meniscus will often dictate how the knee will be managed (e.g. rehabilitation, surgery, etc.).
Some symptoms that people with meniscus injuries may experience include:
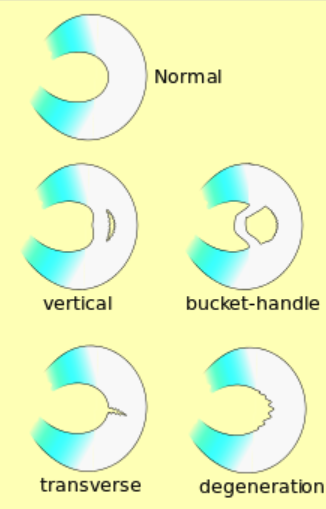
Image 2. Different types and locations of meniscus tears. Source
Fractures (e.g. patella and femur fractures)
Fractures are disturbances to the boney areas of varying degrees ranging from a small crack to a complete break. These injuries typically occur with high-impact traumatic incidents such as motor vehicle accidents or falling from a high platform. Some common, occurring fracture sites include the patella, femoral condyles and tibial plateau.
For less severe injuries, surgery may not be required. Instead, you may have to avoid weight-bearing (e.g. walking, standing) by using an assistance walking device and/or brace. However, more severe fractures will require surgery as deemed appropriate by an orthopedic specialist.
Like the other knee injuries, your symptoms will depend on the location and severity of the injury. Some common signs of a fracture will be localized pain when weight-bearing and immediate pain after a traumatic event.
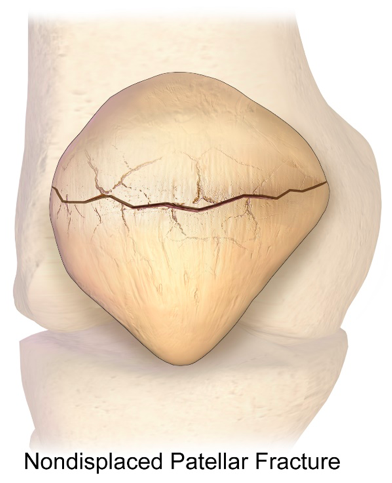
Image 3. A graphical representation of a kneecap fracture. Source
Diagnosis
As the knee is composed of many different structures, it may be difficult to differentiate what injury you may have sustained. To ensure you receive a proper diagnosis and early treatment, you must consult a health professional such as a physical therapist, sports physician or medical doctor.
During your assessment, your consulting medical expert will ask you a series of questions and perform a thorough physical examination. Depending on their findings, you may or may not require further investigations such as an x-ray, CT scan or MRI.
Treatment
Depending on your diagnosis, a decision will be made about the most suitable way of managing your condition. Below will be a potential list of treatments that help manage your pain, swelling, function and recovery.
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is generally an essential treatment for most of these knee injuries. Even if you are awaiting surgery, physical therapy will help bridge the gap by rehabilitating your knee injury. Not only will this help you increase strength, balance and function before surgery, but your improvements will help you recover faster from surgery. Depending on your circumstances, your physical therapist may also use other additional forms of modalities, including:
Assistive walking device
Especially with more acute injuries, you may be recommended to use an assistance walking device such as a walking stick or frame temporarily. Not only will this help you move around with less pain but will reduce the irritation to the knee. Your physical therapist will work with you to wean you off the walking device and progress you to your full capacity
Hot/cold pack
Ice and hot packs may be used at different stages of rehabilitation. Cold packs should be considered to help reduce swelling and pain in the earlier phases of your injury. For other problems such as accompanying muscle spasms or knee pain (without swelling), a hot pack can be considered.
Rest and physical activity
Your health professional will indicate how much rest they would recommend and other restrictions after your injuries. However, you will be recommended to keep as physically active as possible to prevent muscle and strength wastage. To ensure that excessive physical activity does not impede your recovery, please consult your physical therapist.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed or recommended to help you tolerate your knee pain. You must consult your medical doctor before taking any medication(s). These include:
Bracing
Depending on the type and severity of knee pain, such as a fracture of the lumbar spine, your healthcare practitioner may recommend wearing a brace temporarily. A brace helps stabilize the knee and prevent the knee from entering vulnerable ranges. Do not brace unnecessarily as this can lead to long-term deficits such as lower limb weakness.
Surgery
Surgery may be required for those who have more severe injuries or are progressing slowly from physical therapy. You will be referred to an orthopedic surgeon by your doctor who will determine your eligibility. Physical therapy is essential for post-surgical recovery and rehabilitation.
Surgery
Surgery is generally the last option for knee injuries. Conservative treatment, such as physical therapy and exercise, should always be attempted where appropriate. If you have exhausted other options or are presenting with a severe injury, this may be the most suitable route for you. Below will be a concise description of 3 common surgeries associated with the above conditions.
1. Click HERE to learn more about ACL Re-construction
Surgeries on the ACL are generally reserved for grade 3 sprains or ruptures. Grade 1 and grade 2 injuries will require physical therapy only. During this surgery, a graft will be transplanted into the location of the previously ruptured ACL. This graft will eventually adapt and reconfigure into your new ACL. Under most circumstances, your graft will be prepared and taken from your body (e.g. hamstring, quadricep, patella tendon, etc.). However, a joint decision between you and your orthopaedic surgeon will help determine where the graft is taken from.
Proceeding your ACL reconstruction, intense physical therapy is required immediately. Without proper rehabilitation, you may bear the risk of poor outcomes or even re-injury. On average, a period of 9-12 months of rehabilitation will be required before resuming your usual activities.
2. Click HERE to learn more about Meniscus Repair
Meniscus repairs will be performed depending on the severity and location of the injury. A joint decision between you, your physical therapist and surgeon should be made to determine your eligibility. For minor tears, your surgeon will create a small incision into the knee before stitching up your injury. However, for more significant injuries, a piece of the meniscus will be shaved or removed to alleviate symptoms.
After your meniscus repair, intense physical therapy is required immediately. Without proper rehabilitation, you may bear the risk of poor outcomes or even re-injury. On average, a period of 5-6 months will be required before resuming your usual activities (e.g. sports, etc.).
3. Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF) of Fractures
Fractures can occur in numerous locations within the knee such as the kneecap, shin (tibia) and thigh bone (femur). For less severe injuries, using a gait aid and/or bracing the knee will be required to facilitate recovery. However, for more severe fractures, surgery may be recommended instead. An ORIF is performed to help bring the pieces of broken bones together and then secured with fixings such as rods, screws and wires.
Physical therapy and rehabilitation will be required post-surgery to ensure optimal recovery. Your outcomes will vary depending on the location of the injury (e.g. around 4 months for the kneecap, 6 months for the shin bone, etc.).
Mike Lombardi Injury Attorneys provide exceptional services and are experienced with workplace and on-road claims. We understand the financial burden of these types of accidents and aim to help you with your compensation. For any additional support or enquiries, please do not hesitate to text Mike Lombardi at 401-600-0000 or visit https://www.lombardilawoffice.com/. We will comprehensively help guide you through your injury and compensation.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is intended for educational purposes only. If you have been diagnosed with a knee injury after a workplace or motor vehicle accident, please contact an appropriate healthcare professional such as a medical doctor or physical therapist.


